Event Source Notifications in Hybrid Applications
improve this page | report issueOverview
Prerequisite: Make sure to read the Push Notifications in Hybrid Applications tutorial first.
Event source notifications are notification messages that are targeted to devices with a user subscription.
While the user subscription exists, MobileFirst Server can produce push notifications for the subscribed user. These notifications can be delivered by the adapter code to all or some of the devices from which the user subscribed.
To learn more about the architecture and terminology of event-source push notifications refer to the Push notification overview tutorial.
Implementation of the push notification API consists of the following main steps:
On the server side:
- Creating an event source
- Sending notification
On the client side:
- Sending the token and initializing the
WLPushclass - Registering the event source
- Subscribing to/unsubscribing from the event source
- Displaying a received messaged
Agenda
Notification API - Server-side
Creating an event source
To create an event source, you declare a notification event source in the adapter JavaScript code at a global level (outside any JavaScript function):
WL.Server.createEventSource({
name: 'PushEventSource',
onDeviceSubscribe: 'deviceSubscribeFunc',
onDeviceUnsubscribe: 'deviceUnsubscribeFunc',
securityTest:'PushApplication-strong-mobile-securityTest'
});
name– a name by which the event source is referenced.onDeviceSubscribe– an adapter function that is invoked when the user subscription request is received.onDeviceUnsubscribe– an adapter function that is invoked when the user unsubscription request is received.securityTest– a security test from theauthenticationConfig.xmlfile, which is used to protect the event source.
An additional event source option:
poll: {
interval: 3,
onPoll: 'getNotificationsFromBackend'
}
poll– a method that is used for notification retrieval.
The following parameters are required:interval– the polling interval in seconds.onPoll– the polling implementation. An adapter function to be invoked at specified intervals.
Sending a notification
As described previously, notifications can be either polled from the back-end system or pushed by one. In this example, a submitNotifications() adapter function is invoked by a back-end system as an external API to send notifications.
function submitNotification(userId, notificationText) {
var userSubscription = WL.Server.getUserNotificationSubscription('PushAdapter.PushEventSource', userId);
if (userSubscription === null) {
return { result: "No subscription found for user :: " + userId };<
}
var notification={};
notification.MPNS={};
var badgeDigit = 1;
notification = WL.Server.createDefaultNotification(notificationText, badgeDigit, {custom:"data"});
//Set Toast notification for MPNS
notification.MPNS.toast={};
notification.MPNS.toast.text1 = "Toast title";
notification.MPNS.toast.text2 = "Toast content";
WL.Server.notifyAllDevices(userSubscription, notification);
return {
result: "Notification sent to user :: " + userId
};
}
The submitNotification function receives the userId to send notification to and the notificationText.
function submitNotification(userId, notificationText) {
A user subscription object contains the information about all of the user’s subscriptions. Each user subscription can have several device subscriptions. The object structure is as follows:
{
userId: 'bjones',
state: {
customField: 3
},
getDeviceSubscriptions: function()[}
};
Next line:
var userSubscription = WL.Server.getUserNotificationSubscription('PushAdapter.PushEventSource', userId);
If the user has no subscriptions for the specified event source, a null object is returned.
if (userSubscription === null) {
return { result: "No subscription found for user :: " + userId };
}
The WL.Server.createDefaultNotification API method creates and returns a default notification JSON block for the supplied values.
var badgeDigit = 1;
var notification = WL.Server.createDefaultNotification(notificationText, badgeDigit, {custom:"data"});
notificationText- The text to be pushed to the device.Badge(number) - A number that is displayed on the application icon or tile (available only in iOS and Windows Phone).custom- Custom, or Payload, is a JSON object that is transferred to the application and that can contain custom properties.
In case of Windows Phone 8 , there are 3 type of MPNS notifications - Raw, Toast and Tile. Raw notifications are visible when the application is in foreground. Toast and Tile notifications are for cases where the application is in background or not running. To see Tile notifications , pin the application to the start screen.
The default notification JSON block returned by WL.Server.createDefaultNotification API method contains notification JSON for Raw and Tile. To send Toast notifications, add the JSON block for Toast notifications:
notification.MPNS.toast={};
notification.MPNS.toast.text1 = "Toast title";
notification.MPNS.toast.text2 = "Toast content";
For more details refer to user documentation on WL.Server.createDefaultNotification API
The WL.Server.notifyAllDevices API method sends notification to all the devices that are subscribed to the user.
WL.Server.notifyAllDevices(userSubscription, notification);
Several APIs exist for sending notifications:
WL.Server.notifyAllDevices(userSubscription, options)- to send notification to all user’s devices.WL.Server.notifyDevice(userSubscription, device, options)- to send notification to a specific device that belongs to a specific user subscription.WL.Server.notifyDeviceSubscription(deviceSubscription, options)- to send the notification to a specific device.
Notification API - Client-side
WL.Client.Push.isPushSupported()– returnstrueif push notifications are supported by the platform, orfalseotherwise.WL.Client.Push.isSubscribed(alias)– returns whether the currently logged-in user is subscribed to a specified event source alias. The call does not connect to the server, it returns the local state.
When a push notification is received by a device, the callback function defined in WL.Client.Push.registerEventSourceCallback is invoked:
function pushNotificationReceived(props, payload) {
alert("pushNotificationReceived invoked");
alert("props :: " + JSON.stringify(props));
alert("payload :: " + JSON.stringify(payload));
}
If the application was in background mode (or inactive) when the push notification arrived, this callback function is invoked when the application returns to the foreground.
Sample application
Click to download the MobileFirst project.
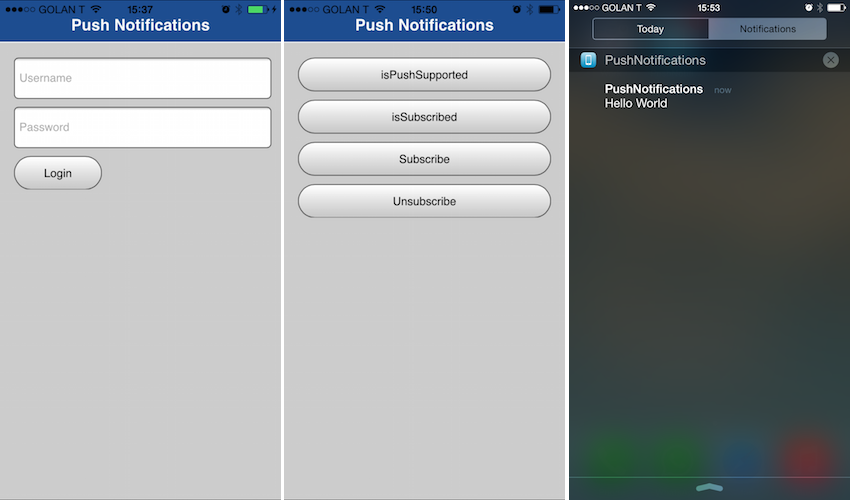
Sending a notification
To test the application is able to receive a push notification you can perform one of the following:
- Right-click the adapter in MobileFirst Studio and select Call MobileFirst Adapter
- If using the CLI, for example:
$ mfp adapter call [?] Which endpoint do you want to use? PushAdapter/submitNotification [?] Enter the comma-separated parameters: "the-user-name", "hello!" [?] How should the procedure be called? GET - The sample application for this tutorial is also bundled with a back-end emulator which can be used to simulate push notification submissions by a back-end system. The source for the emulator is also bundled.
To use the back-end emulator: open the PushBackendEmulator folder in a command prompt/terminal and run the supplied JAR file by using the following syntax.
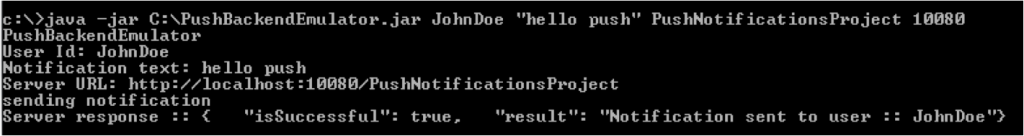
java –jar PushBackendEmulator.jar <userId> <message> <contextRoot> <port>userIdis the user name that you used to log in to the sample application.
contextRootis the context root of your MobileFirst project.Example
java –jar PushBackendEmulator.jar JohnDoe “My first push notification” myContextRoot 10080The back-end emulator tries to connect to a MobileFirst Server and call a
submitNotification()adapter procedure. It outputs the invocation result to a command prompt console.Success
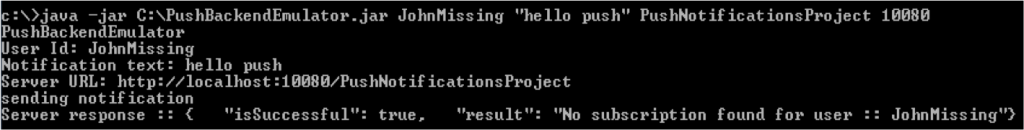
Failure
Inclusive terminology note: The Mobile First Platform team is making changes to support the IBM® initiative to replace racially biased and other discriminatory language in our code and content with more inclusive language. While IBM values the use of inclusive language, terms that are outside of IBM's direct influence are sometimes required for the sake of maintaining user understanding. As other industry leaders join IBM in embracing the use of inclusive language, IBM will continue to update the documentation to reflect those changes.