Android 애플리케이션에서 인증 확인 핸들러 구현
improve this page | report issue개요
보호된 자원에 액세스를 시도할 때 서버(보안 검사)는 처리할 클라이언트에 대한 하나 이상의 인증 확인을 포함하는 목록을 클라이언트에 다시 전송합니다.
이 목록은 추가 데이터의 선택적 JSON과 함께 보안 검사 이름을 나열하는 JSON 오브젝트로 수신됩니다.
{
"challenges": {
"SomeSecurityCheck1":null,
"SomeSecurityCheck2":{
"some property": "some value"
}
}
}
그런 다음 클라이언트는 각 보안 검사에 대해 인증 확인 핸들러를 등록해야 합니다.
인증 확인 핸들러는 보안 검사에 특정한 클라이언트 측 동작을 정의합니다.
인증 확인 핸들러 작성
인증 확인 핸들러는 로그인 화면 표시, 인증 정보 수집, 인증 정보를 보안 검사에 다시 제출과 같이 MobileFirst Server에서 전송한 인증 확인을 처리하는 클래스입니다.
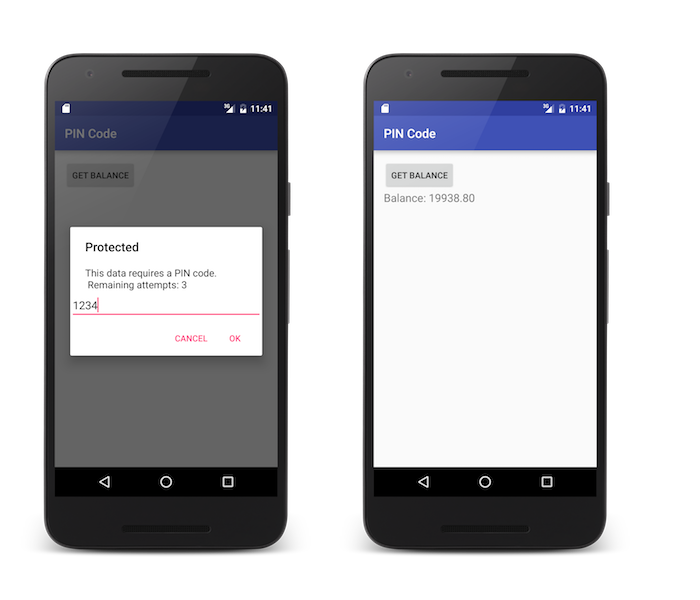
이 예제에서 보안 검사는 PinCodeAttempts이며 CredentialsValidationSecurityCheck 구현에 정의되어 있습니다. 이 보안 검사가 전송한 인증 확인은 남은 로그인 시도 횟수(remainingAttempts) 및 선택적 errorMsg를 포함합니다.
SecurityCheckChallengeHandler를 확장하는 Java 클래스를 작성하십시오.
public class PinCodeChallengeHandler extends SecurityCheckChallengeHandler {
}
인증 확인 처리
SecurityCheckChallengeHandler 프로토콜의 최소 요구사항은 생성자와 handleChallenge 메소드를 구현하는 것으로 사용자가 인증 정보를 제공하도록 프롬프트가 표시됩니다. handleChallenge 메소드는 JSONObject로서 인증 확인을 수신합니다.
생성자 메소드를 추가하십시오.
public PinCodeChallengeHandler(String securityCheck) {
super(securityCheck);
}
이 handleChallenge 예제에서 PIN 코드를 입력하도록 경보가 사용자에게 프롬프트로 표시됩니다.
@Override
public void handleChallenge(JSONObject jsonObject) {
Log.d("Handle Challenge", jsonObject.toString());
Log.d("Failure", jsonObject.toString());
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction(Constants.ACTION_ALERT_MSG);
try{
if (jsonObject.isNull("errorMsg")){
intent.putExtra("msg", "This data requires a PIN code.\n Remaining attempts: " + jsonObject.getString("remainingAttempts"));
broadcastManager.sendBroadcast(intent);
} else {
intent.putExtra("msg", jsonObject.getString("errorMsg") + "\nRemaining attempts: " + jsonObject.getString("remainingAttempts"));
broadcastManager.sendBroadcast(intent);
}
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
alertMsg의 구현이 샘플 애플리케이션에 포함됩니다.
인증 정보가 올바르지 않은 경우, 프레임워크가 다시 handleChallenge을 호출할 것으로 예상할 수 있습니다.
인증 확인 응답 제출
인증 정보를 UI에서 수집한 후에는 SecurityCheckChallengeHandler의 submitChallengeAnswer(JSONObject answer) 메소드를 사용하여 응답을 보안 검사로 다시 전송하십시오. 이 예제에서 PinCodeAttempts는 제출된 PIN 코드를 포함하는 pin이라는 특성을 예상합니다.
submitChallengeAnswer(new JSONObject().put("pin", pinCodeTxt.getText()));
인증 확인 취소
UI에서 취소 단추를 클릭한 것처럼 일부 경우에 이 인증 확인을 완전히 버리도록 프레임워크에 알리고자 할 수 있습니다.
이를 위해서는 SecurityCheckChallengeHandler의 cancel() 메소드를 사용하십시오.
실패 처리
일부 시나리오에서는 실패를 트리거합니다(예: 최대 시도 횟수에 도달). 이를 처리하려면 SecurityCheckChallengeHandler의 handleFailure 메소드를 구현하십시오.
매개변수로 전달된 JSONObject의 구조는 실패의 특성에 크게 좌우됩니다.
@Override
public void handleFailure(JSONObject jsonObject) {
Log.d("Failure", jsonObject.toString());
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction(Constants.ACTION_ALERT_ERROR);
try {
if (!jsonObject.isNull("failure")) {
intent.putExtra("errorMsg", jsonObject.getString("failure"));
broadcastManager.sendBroadcast(intent);
} else {
intent.putExtra("errorMsg", "Unknown error");
broadcastManager.sendBroadcast(intent);
}
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
alertError의 구현이 샘플 애플리케이션에 포함됩니다.
성공 처리
일반적으로 애플리케이션의 남은 부분이 계속 실행될 수 있도록 프레임워크에서 성공을 자동으로 처리합니다.
선택적으로 SecurityCheckChallengeHandler의 handleSuccess 메소드를 구현하여 프레임워크가 인증 확인 핸들러 플로우를 닫기 전에 작업하도록 선택할 수 있습니다. 여기에서 다시, 매개변수로 전달된 JSONObject의 컨텐츠와 구조는 보안 검사가 전송한 항목에 따라 달라집니다.
PinCodeAttempts 샘플 애플리케이션에서 JSONObject는 추가 데이터를 포함하지 않으므로 handleSuccess가 구현되지 않습니다.
인증 확인 핸들러 등록
인증 확인 핸들러가 올바른 인증 확인을 청취하도록 프레임워크에 특정 보안 검사 이름과 인증 확인 핸들러를 연관시키도록 알려야 합니다.
이를 위해서 다음과 같이 보안 검사를 사용하여 인증 확인 핸들러를 초기화하십시오.
PinCodeChallengeHandler pinCodeChallengeHandler = new PinCodeChallengeHandler("PinCodeAttempts", this);
그런 다음 인증 확인 핸들러 인스턴스를 등록해야 합니다.
WLClient client = WLClient.createInstance(this);
client.registerChallengeHandler(pinCodeChallengeHandler);
참고: WLClient 인스턴스 작성 및 인증 확인 핸들러 등록은 전체 애플리케이션 라이프사이클에서 한 번만 일어나야 합니다. Android 애플리케이션 클래스를 사용하여 수행할 것을 권장합니다.
샘플 애플리케이션
샘플 PinCodeAndroid는 은행 잔고를 얻기 위해 WLResourceRequest를 사용하는 Android 애플리케이션입니다.
메소드는 최대 3번의 시도로 PIN 코드로 보호됩니다.
SecurityAdapters Maven 프로젝트를 다운로드하려면 클릭하십시오.
Android 프로젝트를 다운로드하려면 클릭하십시오.
샘플 사용법
샘플의 README.md 파일에 있는 지시사항을 따르십시오.
Inclusive terminology note: The Mobile First Platform team is making changes to support the IBM® initiative to replace racially biased and other discriminatory language in our code and content with more inclusive language. While IBM values the use of inclusive language, terms that are outside of IBM's direct influence are sometimes required for the sake of maintaining user understanding. As other industry leaders join IBM in embracing the use of inclusive language, IBM will continue to update the documentation to reflect those changes.