Application Authenticity Protection
improve this page | report issueOverview
By issuing an HTTP request, any entity can access the HTTP services (APIs) that IBM MobileFirst Platform Foundation Server offers.
The Application Authenticity Protection feature ensures that an application that tries to connect to a MobileFirst Server instance is the authentic one and was not tampered with or modified by a third-party attacker.
Application authenticity protection is available for:
- Android: native and hybrid
- iOS: native and hybrid
- Windows Universal: native and hybrid
- Windows Phone Silverlight 8: hybrid only
Note:
Application Authenticity Protection is not available in the MobileFirst Development Server. To test, deploy the application to a MobileFirst Server instance on a remote application server.
Agenda
Authenticity flow and types
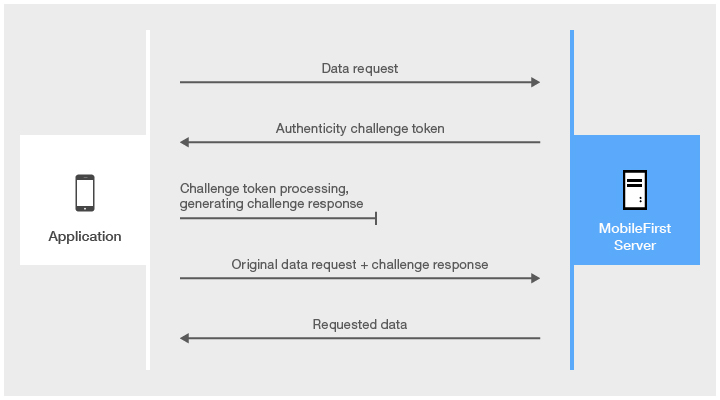
The challenge token is processed by compiled native code, so that third-party attackers cannot see the logic of this processing.
Application Authenticity Protection is based on certificate keys that are used to sign the application bundles.
Only the developer or the enterprise who have the original private key that was used to create the application are able to modify, repackage, and re-sign the bundle.
Three levels of authenticity are available:
- No Authenticity
- Basic Authenticity
- Extended Authenticity (Provides a more detailed verification and is more secured)
Setting up authenticity
To set up application authenticity protection, you go through the following two steps:
Project-level setup
Whether you want Basic or Extended authenticity protection, the following setup steps are required.
Extended authenticity protection requires additional setup steps, which are explained in the Enabling extended protection section.
Modify the authenticationConfig.xml configuration file
- Add the relevant authentication realm to a security test.
- If a
mobileSecurityTestis used, add thetestAppAuthenticitychild element to it:
<mobileSecurityTest name="MyMobileAuthenticityTest"> <testAppAuthenticity/> <testDeviceId provisioningType="none" /> <testUser realm="myMobileLoginForm" /> </mobileSecurityTest> - If a
customSecurityTestis used, add thewl_authenticityRealmrealm to it:
<customSecurityTest name="MyCustomAuthenticityTest"> <test realm="wl_authenticityRealm" step="1"/> <test realm="wl_anonymousUserRealm" isInternalUserID="true" step="1"/> <test realm="wl_deviceNoProvisioningRealm" step="2" isInternalDeviceID="true"/> </customSecurityTest>
- If a
- After you have configured the authenticity realm and security check, go to Environment-specific setup and select your environment to complete the authenticity configuration.
Enabling extended application authenticity protection
To enable extended authenticity checking, you must deploy a modified .wlapp file, instead of the original .wlapp file that is generated by the build process.
- Modify the
.wlappfile by using thewladmprogram or thewladmAnt task: - By using the
wladmprogram
Use thewladmprogram (provided in the MobileFirst installation directory) to run theenable extended-authenticitycommand:
wladm enable extended-authenticity src-wlapp-file device-file > dest-wlapp-filesrc-wlapp-file=> Original binary app file (.wlapp)device-file=> Binary mobile app file (.apk,.ipa, or.xap)dest-wlapp-file=> Output binary app file (.wlapp)
After running the
wladm, deploy the resulting file to the MobileFirst Server instance. - By using the
wladmAnt task
Use thewladmAnt task (provided in the MobileFirst installation directory) to run theenable-extended-authenticitycommand:
<enable-extended-authenticity srcwlappfile="original-.wlapp-file" devicefile="device file(.apk, .ipa, or .xap)" destwlappfile="output-.wlapp-file"/> - After running the
wladmcommand or Ant task, deploy the resulting file to MobileFirst Server instance.
You can use the MobileFirst Operations Console to see the authenticity level of an application.
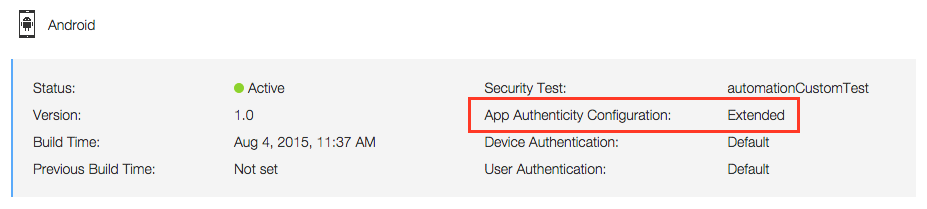
For more information, see the topic about configuring extended app authenticity checking, in the user documentation.
Environment-specific setup
For basic authenticity, go through the basic configuration steps.
For extended authenticity, it is recommended to make these extra configuration changes.
- Application Authenticity Protection in Hybrid applications
- Application Authenticity Protection in Native Windows Universal applications
- Application Authenticity Protection in Native Android applications
- Application Authenticity Protection in Native iOS applications
Inclusive terminology note: The Mobile First Platform team is making changes to support the IBM® initiative to replace racially biased and other discriminatory language in our code and content with more inclusive language. While IBM values the use of inclusive language, terms that are outside of IBM's direct influence are sometimes required for the sake of maintaining user understanding. As other industry leaders join IBM in embracing the use of inclusive language, IBM will continue to update the documentation to reflect those changes.